How to distinguish the members of crocodilians?
本文同时提供以下语言的翻译: Chinese
To most people, the alligators and members of the crocodilians look very similar, and they do share many characteristics, but if you pay attention to a few details, you can see their differences.
“Crocodilia (scientific name: Crocodilia) is commonly known as crocodiles, belongs to the phylum chordate lizards class.Distributed in tropical to subtropical rivers, lakes, and coasts, 24 species are present.”– From the Encyclopedia
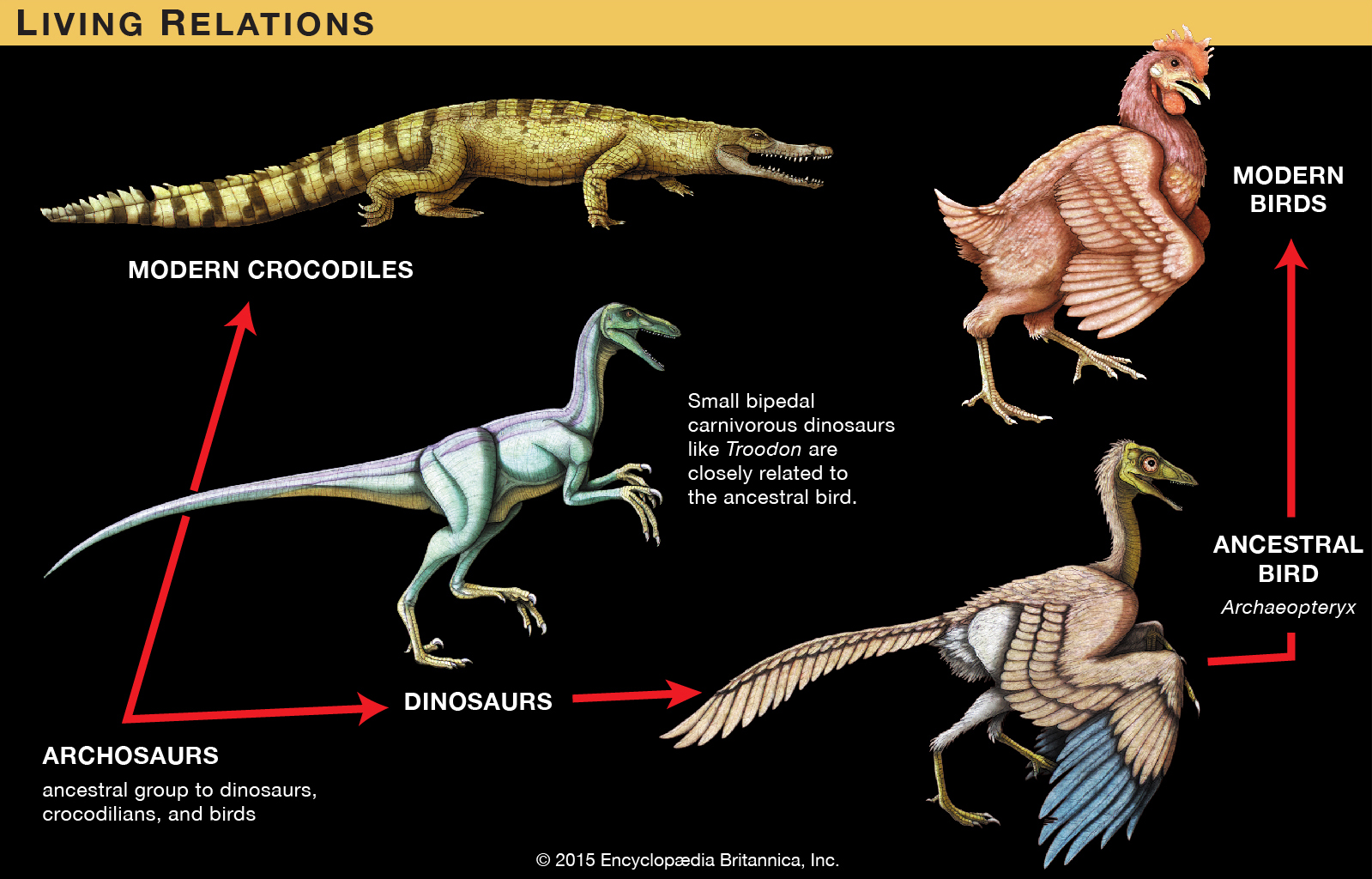
As a family of crocodiles dating as far back as the late Triassic (Crocodylidae) and flourishing in the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, they are at the top of the ecological chain with their powerful bodies and amphibious (amphibian reptile) characteristics.
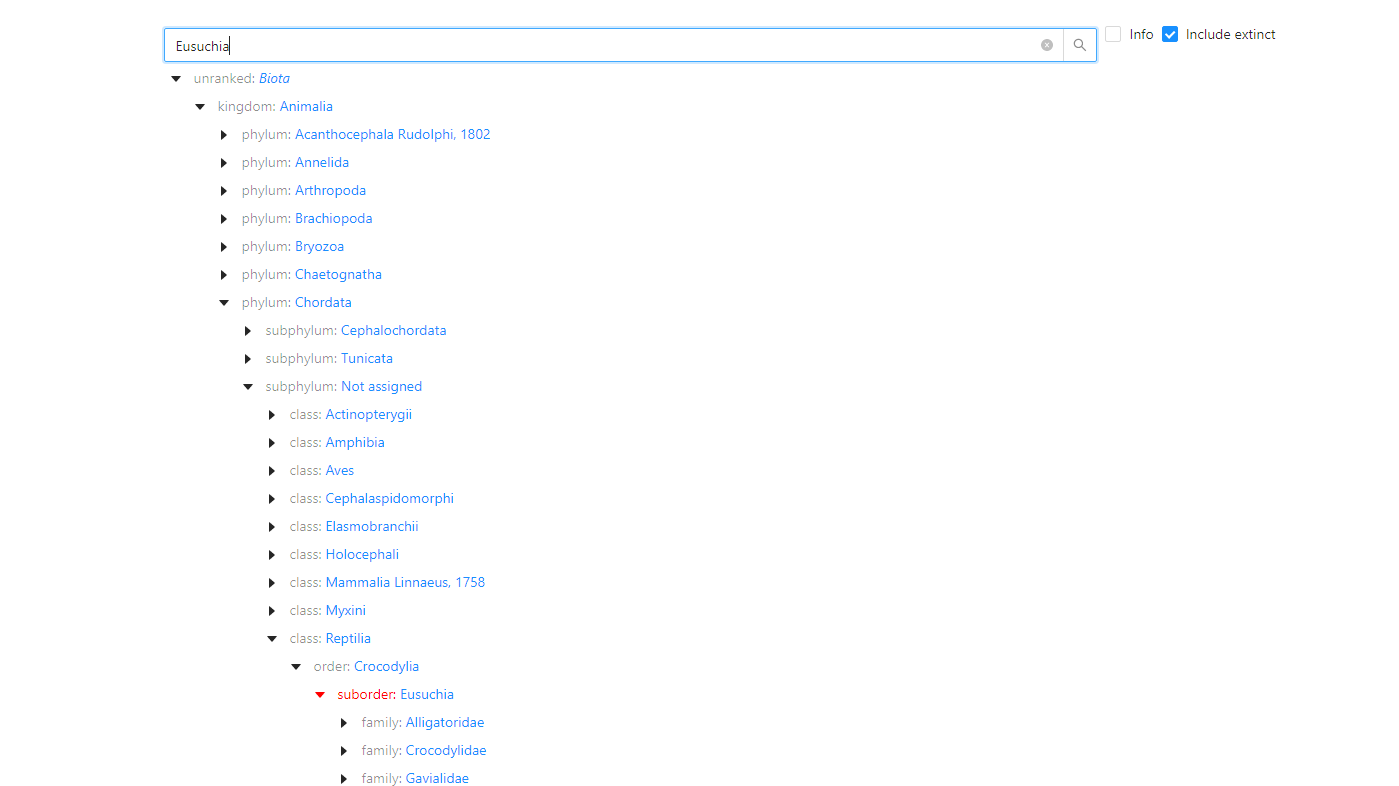
According to the study, there were about 150 genera of crocodiles during that time, whereas today there are only 26 species in eight genera.It is important to distinguish, however, that the Latin scientific name for what we now call crocodiles is Eusuchia, which translates as’ true crocodilians’.
Late Cretaceous and distinct from ‘primitive’ crocodiles: a complete secondary palate formed from the maxilla, upper jaw, and wing bones, among other cranial features.
After the Cenozoic Miocene in earth’s history, the climate gradually began to become dry, and the tropical rain forests that used to cover the world gradually turned into grasslands.
All this had a huge impact on land animals, with many new dry-adapted mammals such as cats and bears rapidly rising to the top of the food chain.Poor adaptation to climate change and strong competition caused by the end of the Miocene,
Almost all of the world’s large terrestrial crocodiles and quite a few amphibious ones have been lost.
Classify
Anyway, crocodilians today fall into three large families: Crocodylidae, Alligatoridae, and Gavialidae.
To give you an intuition, I’ll include a complete overview of modern categories at the end of the article.
The differences between members of alligator family and crocodilians
First, members of the Alligator family, is a word we have heard so well in primary school.They are mainly found in Africa, Asia,
Tropical regions of America and Australia that tend to gather in fresh water such as rivers, lakes, and marshes.Sometimes they live in half water (alligators).PS: It is also a good choice to judge according to geographical location and population distribution.
In general, crocodiles (crocodilians) are more aggressive than alligators, making them more dangerous than alligators. Alligators are opportunistic predators, which means they generally won’t go after you unless provoked.
(PPS: It is better to observe under the premise of absolute safety ( ̄,  ̄))
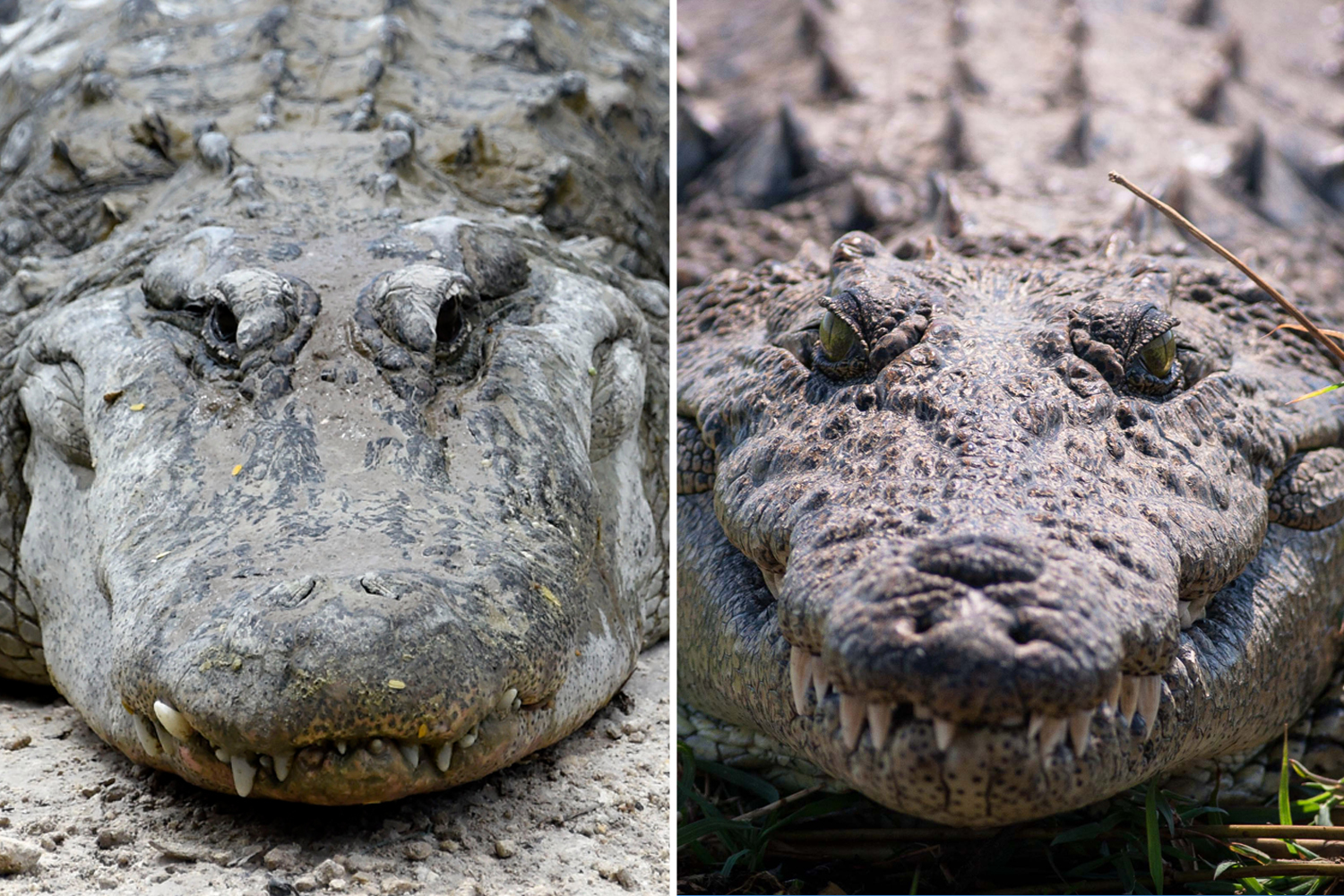
The beak and jawline may be the easiest way to distinguish an alligator from an alligator, but some species have exceptions that can be deceptive.
- Beak: Alligators have wide, round, U-shaped jaws, while crocodiles have long, pointed, V-shaped jaws.
- Jaw line: Alligators have a wide upper jaw so their teeth can be hidden in the mouth.Crocodiles and alligators are different in that they have nearly the same size jaws.
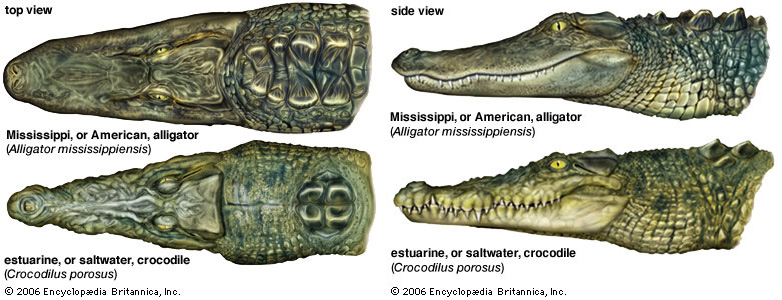
From top to bottom: American alligator, black caiman (Alligator family), American Alligator
Another way to tell them apart is by looking at their teeth. Crocodilians are definitely marked by the protruding fourth or sixth jaw tooth, which is long and vertical, so that they have a special opening in the upper jaw that fits in with the tooth when they are shut up.
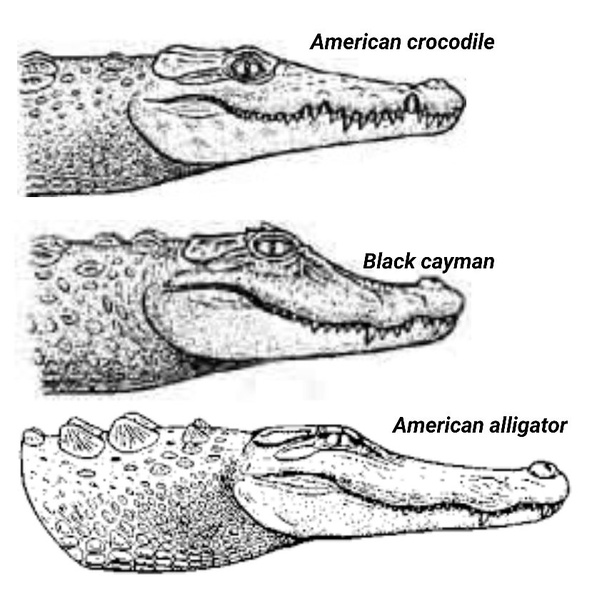
In Subfamily Gufurinae and Subfamily Caiman, members of Subfamily Gufurinae do not show their lower teeth when their upper and lower jaws are closed, while in some members of Subfamily Caiman, due to “violent growth” in adulthood, some of them show their lower teeth when they shut up.【 1 】
However, in spite of the violent growth, alligator members do not have a dent in their upper jaw to avoid teeth, so in the wild, it is sometimes observed that the lower teeth of the Alligator Pierce the skin of the upper jaw and continue to grow.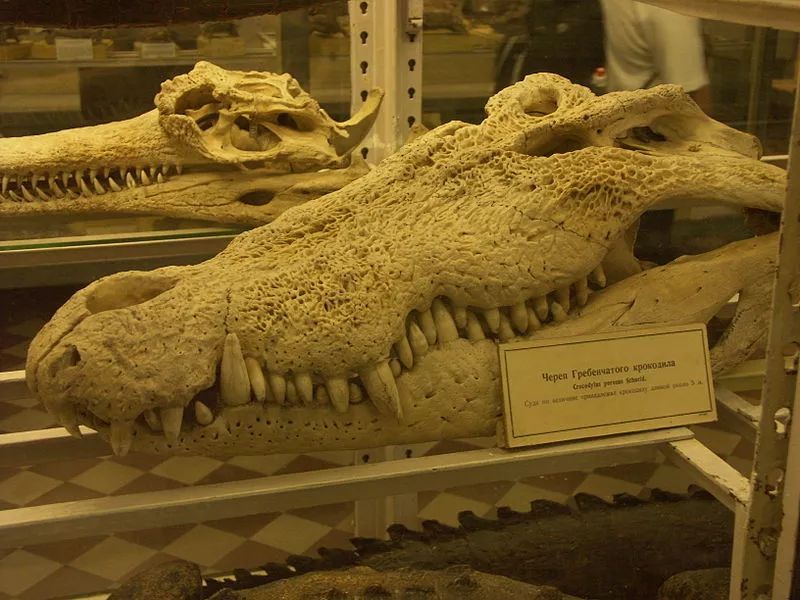
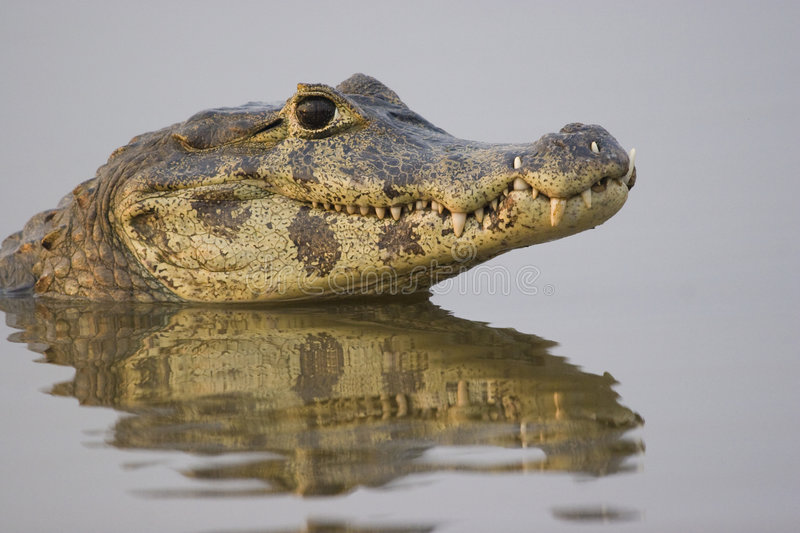

(Caiman with overgrown teeth)
Neck shield is also a distinction between alligator and a large standard.The necks of all members of the Alligator family extend continuously from the back of the head to the back.However, there is no shield in the back of the head of eucroc members, and the cervical shield and dorsal shield fragments are separated and discontinuous.
According to the neck shield of the crocodile can even be more specific to determine the species of the crocodile, here will not elaborate.
Conclusion
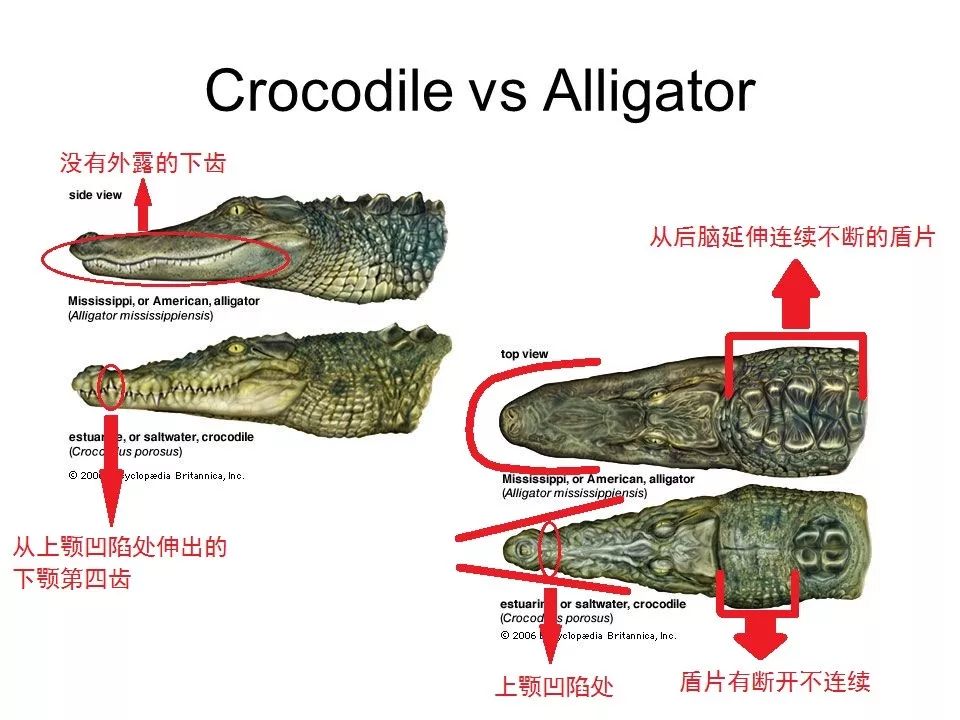
In comparison, the top of the picture shows The Mihe Alligator (Alligator) in alligator family, and the bottom shows the bayalligator in alligator family.The side view shows no exposed lower teeth of Mihe Alligator,
The crocodile not only has its lower teeth exposed, but also has a very long fourth tooth in its lower jaw.
In the top view, the U-shaped snout of the alligator and the V-shaped snout of the alligator can be clearly observed, as well as the obvious depression in the upper jaw of the alligator.
At the same time, we can also see the neck shield of the Mihe Alligator continuously from the back of the head, while the bay alligator has a bare disconnect part.【 2 】
Gavialidae, the last of the three is the easiest to distinguish, with an extremely long snout and a regular interlocking of upper and lower teeth.Due to the close relationship with eucrocidae, their cervical and dorsal shields are also discontinuous.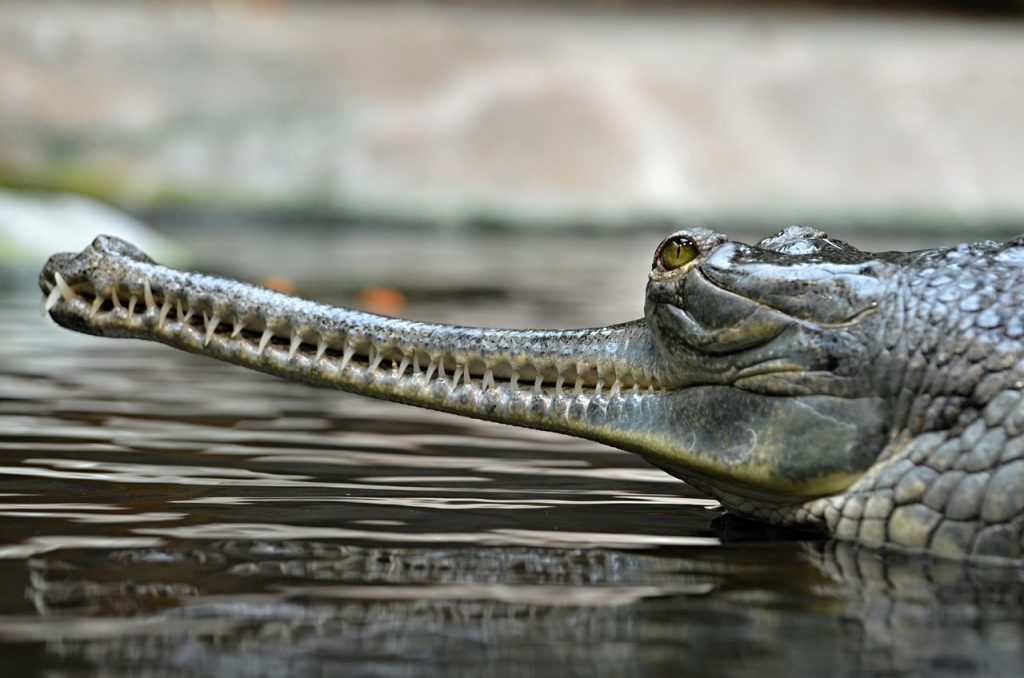
Finally, put up a photo of the three members of the unit for comparison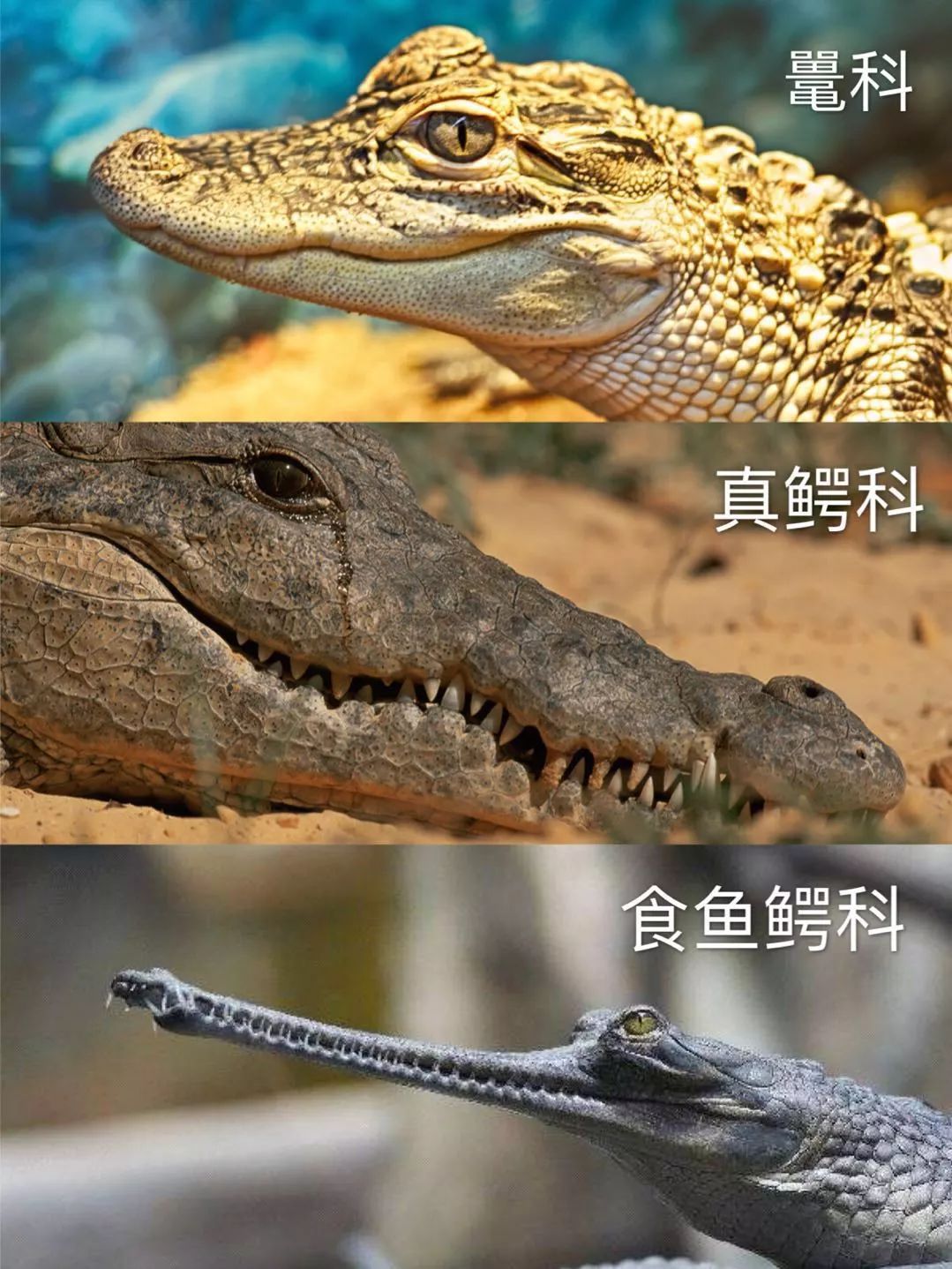
Modern classification
鼍科(短吻鳄科) Alligatoridae
- 鼍亚科 Alligatorinae
- 鼍属 Alligator
- 鼍(扬子鳄 Alligator sinensis
- 密河鳄 Alligator mississippiensis
- 鼍属 Alligator
- 凯门鳄亚科 Caimaninae
- 凯门鳄属 Caiman
- 眼镜凯门鳄 Caiman crocodilus
- 巴拉圭凯门鳄 Caiman yacare
- 宽吻凯门鳄 Caiman latirostros
- 古鳄属 Paleosuchus
- 钝吻古鳄 Paleosuchus palpebrosus
- 锥吻古鳄 Paleosuchus trigonatus
- 黑鳄属 Melanosuchus
- 黑凯门鳄 Melanosuchus niger
- 凯门鳄属 Caiman
真鳄科 Crocodylidae
- 鳄亚科 Crocodylinae
- 鳄属 Crocodylus
- 美洲鳄 Crocodylus acutus
- 非洲狭吻鳄 Crocodylus cataphractus
- 奥利诺科鳄 Crocodylus intermedius
- 澳洲淡水鳄 Crocodylus johnstoni
- 菲律宾鳄 Crocodylus mindorensis
- 危地马拉鳄(莫瑞雷鳄) Crocodylus moreletii
- 尼罗鳄 Crocodylus niloticus
- 新几内亚鳄 Crocodylus novaeguineae
- 沼泽鳄 Crocodylus palustris
- 湾鳄 Crocodylus porosus
- 古巴鳄 Crocodylus rhombifer
- 暹罗鳄 Crocodylus siamensis
- 西非尼罗鳄Crocodylus suchus
- 侏鳄属 Osteolaemus
- 侏鳄 Osteolaemus tetraspis
- 狭吻鳄属 Mecistops
- 非洲狭吻鳄 Mecistops cataphractus
- 细嘴狭吻鳄 Mecistops leptorhynchus
- 鳄属 Crocodylus
食鱼鳄科(长吻鳄科) Gavialidae
- 切喙鳄属 Tomistoma
- 马来长吻鳄 Tomistoma schlegelii
- 长吻鳄属 Gavialis
- 恒河鳄 Gavialis gangeticus
- 恒河鳄 Gavialis gangeticus
Citation
Everglands,The Difference Between Alligators and Crocodiles,https://www.evergladesholidaypark.com/alligators-and-crocodiles/#:~:text=Physical%20Differences&text=Snout%20Shape%3A%20Alligators%20have%20a,%2Dshelled%20vertebrates%2C%20like%20turtles. July,12,2021
Schwimmer, David R. The Size of Deinosuchus. King of the Crocodylians: The Paleobiology of Deinosuchus. Indiana University Press. July,11,2021
James P. Ross. Heinz Fritz Wermuth, Evolution and classification, Britannica,https://www.britannica.com/animal/crocodile-order/Evolution-and-classification, July,11,2021
Paxingtianxia,(Crocodile face blindness treatment paste) take you to distinguish 24kinds of crocodiles in the world (upper · true crocodile family), freewechat, https://freewechat.com/a/MzI1Nzc3OTE1OA==/2247514655/1, July,12,2021
注【1】【2】摘自爬行天下,【鳄鱼脸盲症治疗贴】带你分清全世界24种鳄鱼(上 · 真鳄科)
How to distinguish the members of crocodilians?





