The concept of Taxonomy
本文同时提供以下语言的翻译:中文
Some time ago, we learned the characteristics of the members of the three families of crocodilians and the methods to distinguish them.The most basic and important reference is biological classification.
Biological classification is a method of grouping and classifying species of living organisms using the methods of taxonomic classification. The familiar domains, kingdoms, phyla, classes, orders, families, genera, and species are the quantitative hierarchies used in the structures based on hierarchies.
Here, I would like to introduce you to the basic concepts and history of biological classification.
What is Taxonomy
Biological taxonomy is a subject about the principles and methods of identification, classification and nomenclature of biological individuals.
The scope of biological taxonomy includes: studying the degree of similarities and differences between groups of organisms, and clarifying the kinship, evolutionary process and development law of organisms.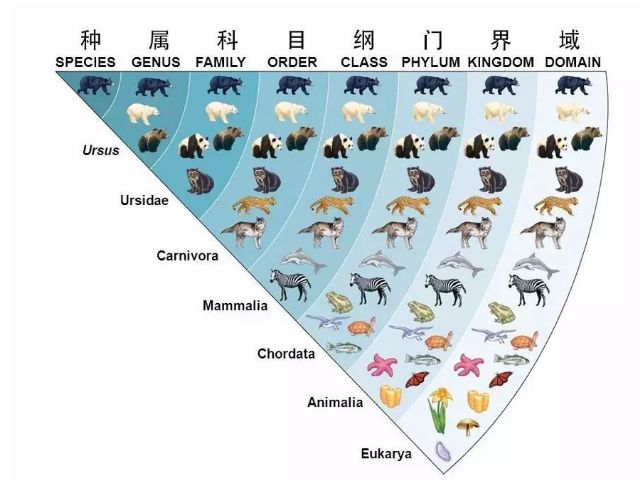
Basis of classification
Having said all this, perhaps the most curious thing is how we classify the world’s many species.
–Biological classification is mainly based on the morphological structure, physiological function of organisms.At the same time, it can also be used as a reference according to the habitat and geographical location.
Here’s an example of classification based on morphological structure:
For example, anatomically, man, monkey, sheep, Dogs all have segmented vertebrae and therefore belong to the subphylum vertebrates.In contrast, some animals, such as the wenchang fish (subphylum cephalochords), have only one unjointed bone on their back,
and these species with the bones in the back are grouped into the phylum Chordates.
Kelp, for example, is no longer classified as a plant because it has been found that its chloroplasts have four membranes, whereas plant chloroplasts have two.
It turns out that the kelp’s ancestor was a creature with four-membraned chloroplasts, distant from what we think of as plants.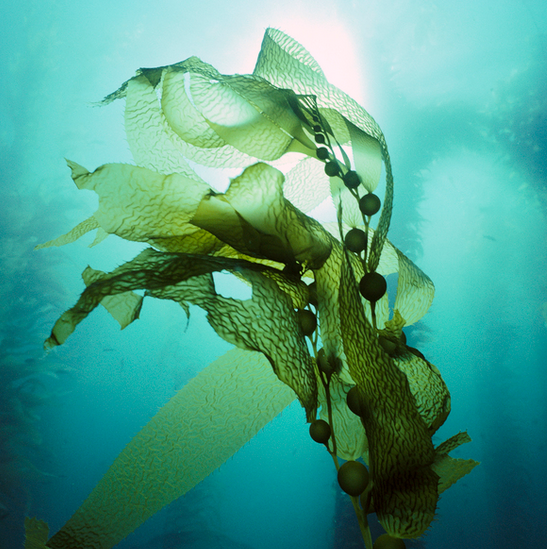
The concept of the quantitative level of classification
specie is a basic unit in the taxonomic system of living things, having a common genetic makeup (and thus a common ancestor, similar shape, internal structure, behavior, etc.),
Having a relatively stable and distinct boundary that distinguishes it from other species.Related species are grouped into genera, related genera into families, families into orders, orders into classes, classes into phyla, and phyla into kingdoms. Organisms with the same or similar morphological structure are more closely related, and organisms of the same species can mate in a natural state and produce fertile offspring.
The history and significance of biological classification
The significance of biological classification is to clarify the kinship and evolutionary relationship between different groups.
The earliest known classification system for life forms was established by the Greek philosopher Aristotle.He classified animals according to the way they moved (in the air, on land or in the water).
In China, Li Shizhen (c. 1518-1593) of the Ming Dynasty, in the pharmacopoeia Compendium of Materia Medica (Compendium of Materia Medica), divided biological medicinal materials into grass, grain, vegetable, fruit, wood, worm, scale, mesophyll, poultry, animal and human.Conrad Gesner (1516 – 1565), a Swiss professor, made an analytical generalization of the known organisms at that time.
The discovery of the New World brought many novel descriptions and specimens of animal species to Europe.In the late 16th and early 17th centuries, detailed descriptions of animals began, first of familiar species, and then gradually expanded until a sufficiently large body of knowledge based on anatomy was formed.
This anatomical knowledge was primarily derived from medical anatomists, and was later expanded by entomologists and the first microscopists.
The father of modern taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus’s great book “Natural Systems” was adapted 12 times during his lifetime.In this book, nature is divided into three kingdoms: mineral, plant and animal.Linnaeus used four classes of classification: class, order, genus and species.
Linnaeus also established scientific names for all species that are still used today.Before Linnaeus, naming a species required long, multi-word names that included a description of the species, and these names were not fixed.Linnaeus separated nomenclature and taxonomy by unifying species names into two-word Latin names, known as scientific names.
This method of naming organisms is called binomial nomenclature.
Only later did biologists classify them by Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species.
That’s all for this article, and finally, heres the link of biological classification levels andSummary table of biological classification
Reference
1.中国大百科智慧藏:分类学
2. Linnaeus, Carolus. Systema naturae per regna tria naturae :secundum classes, ordines, genera, species, cum characteribus, differentiis, synonymis, locis 10th. Stockholm: Laurentius Salvius. 1758
3. Linnaeus, C. Systemae Naturae, sive regna tria naturae, systematics proposita per classes, ordines, genera & species. 1735.
4. Wikipedia,Taxonomy (biology),8,22,2021
5. Zhihu,2021,8,22
The concept of Taxonomy




